Comprehensive Guide to Essential Shell Scripting Commands
Table of contents
No headings in the article.
This documentation serves as a comprehensive guide to essential shell scripting commands, providing step-by-step explanations and practical examples for each command.
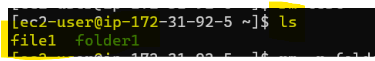
ls: Lists directory contents.
Explanation: The
lscommand is used to list the files and directories within a specified directory.Example:
lsThis command will list all the files and directories in the current directory.
pwd: Prints the current working directory.
Explanation:
pwdstands for "print working directory." It displays the full path of the current working directory.Example:
pwd
Running this command will print the current directory's absolute path.
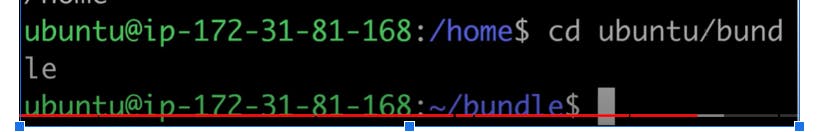
cd: Changes the current directory.
Explanation: The
cdcommand allows you to change the current working directory to the specified directory.Example:
cd /path/to/directoryThis command will change the current directory to the one specified.
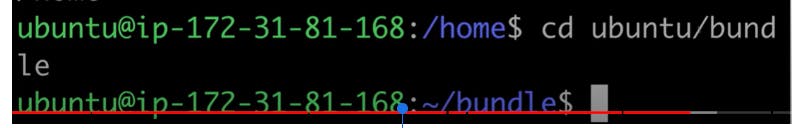
cd .. : Moves up one directory level in the directory tree.
Explanation:
cd ..allows you to move one level up in the directory structure.(It will go back from one folder)Example:
cd ..Running this command will move you up one directory level.
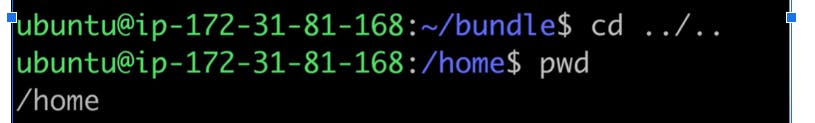
cd ../..: Moves up two directory levels in the directory tree.
Explanation: This command moves you up two levels in the directory structure.(It will go back from 2 folders)
Example:
cd ../..Running this command will move you up two directory levels.
cd folder1/folder2: Changes to a directory within the current directory.
Explanation: You can change to a directory within the current directory by specifying its path.
Example:
cd documents/scriptsThis command will change the current directory to "scripts" within the "documents" directory.
ls -ltr: Lists files in long format sorted by modification time.
Explanation: The
-ltroption displays files in long format, sorted by modification time in reverse order.It provides the information about that file or folder along with timestamp
if its starting with ‘d’ then it is directory or else file
Example:
ls -ltrRunning this command will list files in long format sorted by modification time, with the newest files appearing last.
vi: Opens the vi text editor.
Explanation:
viis a text editor used to create or edit files.Example:
vi filename.txtThis command will open the vi text editor and create/edit the file named "filename.txt".
cat: Concatenates and displays file content.
Explanation:
catis used to display the contents of one or more files.Example:
cat filename.txtThis command will display the contents of the file named "filename.txt".
mkdir: Creates a new directory.
Explanation:
mkdiris used to create a new directory.Example:
mkdir new_directory
rm filename: Removes a file.
Explanation:
rmis used to remove/delete a file.Example:
rm file.txtThis command will remove the file named "file.txt".
rm -r foldername: Removes a directory recursively.
Explanation:
rm -ris used to remove a directory and its contents recursively.Example:
rm -r directoryThis command will remove the directory named "directory" and all its contents.

nproc: Prints the number of processing units available.
Explanation:
nprocdisplays the number of processing units (CPU cores) available on the system.Example:
nprocThis command will print the number of CPU cores available.
free -g: Displays the amount of free and used memory in gigabytes.
Explanation:
free -gshows the system's memory usage in gigabytes.Example:
free -gThis command will display memory usage in gigabytes.
df -h: Displays disk space usage in a human-readable format.
Explanation:
df -hshows disk space usage in a human-readable format.Example:
df -hThis command will display disk space usage in a human-readable format.
top: Displays real-time system information.
Explanation:
topprovides real-time information about system processes, CPU usage, and memory usage.Example:
top
This command will display real-time system information
chmod: Changes file permissions.
Explanation:
chmodis used to change the permissions of a file or directory.Example:
chmod 755 filename.txt
This command will change the permissions of the file "filename.txt" to 755
stat -c %a filename: Displays file access rights in octal format.
Explanation:
stat -c %adisplays file access rights in octal format.Example:
stat -c %a filename.txt
This command will display the access rights of the file "filename.txt" in octal format.
man: Displays the manual of a command.
Explanation:
mandisplays the manual pages for a specified command.Example:
man ls
This command will display the manual page for the ls command.
grep: Searches for patterns in files.
Explanation:
grepis a command-line utility for searching plain-text data sets for lines that match a regular expression.Example:
grep "pattern" filename.txt
This command will search for lines containing the specified pattern in the file "filename.txt".
curl: Transfers data to or from a server.
Explanation:
curlis a command-line tool for transferring data with URL syntax. It supports various protocols including HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, etc.Using the curl command we can get the information from the api’s as well just like in python we are doing with the requests module
Example:
curl https://example.com
This command will retrieve the contents of the specified URL.
wget: Downloads files from the internet.
Explanation:
wgetis a command-line utility for downloading files from the web using HTTP, HTTPS, or FTP protocols.Using Wget command it will download that information and save it in the logfile locally
Example:
wget https://example.com/file.txtThis command will download the file "file.txt" from the specified URL.
pipe |: Redirects the output of one command as input to another.
Explanation: The pipe (
|) operator is used to redirect the output of one command as input to another command.Pipe parameter sends the output of the first command to the second command
Pipe command it will receive the information from the stdout not from stdin
Example:
ls | grep "pattern"This command will list files in the current directory and then filter the output to display only the lines containing the specified pattern.
awk -F "" '{print $2}': Processes text files.
Explanation:
awkis a programming language used for pattern scanning and processing.-F ""specifies an empty field separator, and{print $2}prints the second field.Example:
awk -F "," '{print $2}' file.txtThis command will process the text file "file.txt" using comma as a field separator and print the second field of each line.
find / -name filename: Searches for files and directories.
Explanation:
findis a command-line utility for searching files and directories in a directory hierarchy./specifies the starting directory, and-name filenamespecifies the search criteria.Example:
find / -name "file.txt"This command will search for the file named "file.txt" starting from the root directory
/.
shebang: Specifies the interpreter for a script.
Explanation: The shebang (
#!) line at the beginning of a script specifies the interpreter to be used to execute the script.Example:
#!/bin/bashThis shebang line specifies that the script should be executed using the Bash shell.
set -x: Enables tracing of commands and their arguments.
Explanation:
set -xenables debugging mode, where each executed command and its arguments are printed to the terminal.set -x : It will print all the commands on the script in a debug mode
Example:
set -xThis command enables tracing of commands and their arguments.
set -e: Exits immediately if a command exits with a non-zero status.
Explanation:
set -ecauses the script to exit immediately if any command returns a non-zero exit status.set -e : It will exit the script when there is an error in the script
Example:
set -eThis command enables immediate exit on error.
set -o: Displays or sets shell options.
Explanation:
set -odisplays or sets various shell options.We need to use set -o because set -e won’t give any error if the last command in the line is executed successfully. It will fail only if the last command on the line fails
Example:
set -oThis command sets the
nounsetoption, causing an error to occur if