Mastering Load Balancers: A Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up an Application Load Balancer on AWS
Load balancers are the unsung heroes of modern web applications. They distribute incoming traffic across multiple instances, ensuring better performance, high availability, and fault tolerance. In the world of Amazon Web Services (AWS), there are several types of load balancers, but in this blog post, we'll focus on creating an Application Load Balancer (ALB). To illustrate the process, we'll set up an ALB with two target groups, products-target-group and orders-target-group, and deploy a total of six EC2 instances—three in each target group.
Architecture
Here are the detailed steps for setting up an Application Load Balancer (ALB) on AWS with two target groups (products-target-group and orders-target-group) and deploying a total of four EC2 instances (two in each target group)

Prerequisites:
An AWS account with access to EC2, Load Balancer and Target Group.
Basic knowledge of AWS services and EC2 instances, Load Balancers(Classic, Application and Network Load Balancers), Target Group and Security Group.
Why Choose an Application Load Balancer (ALB)?
AWS offers multiple types of load balancers, including the Classic Load Balancer and the Network Load Balancer, but the Application Load Balancer (ALB) stands out for its versatility. It operates at the application layer (Layer 7) and is designed to efficiently route HTTP and HTTPS traffic, making it ideal for modern web applications, microservices, and APIs. ALBs offer advanced routing capabilities, including path-based routing and host-based routing, which can help you manage complex traffic patterns effortlessly.
Layer 7 Load Balancing: ALB operates at the application layer (Layer 7) of the OSI model. It understands HTTP and HTTPS traffic, allowing for advanced routing based on URL paths, hostnames, and headers.
Path-Based Routing: With ALB, you can route requests based on URL paths. This enables you to direct traffic to different sets of backend servers based on the content requested.
Flexible Listener Rules: ALB allows you to create custom routing rules, making it ideal for complex applications and microservices architectures.
Step 1: Launch an Amazon EC2 Instances:
Log in to your AWS Management Console.
Navigate to the EC2 dashboard.
Click "Launch Instance" to create a new 4 EC2 instances for 2 products EC2 instances and 2 orders EC2 instances.
Create products_1 EC2 instance:
- Give a name to the products_1 EC2 instance as products_1
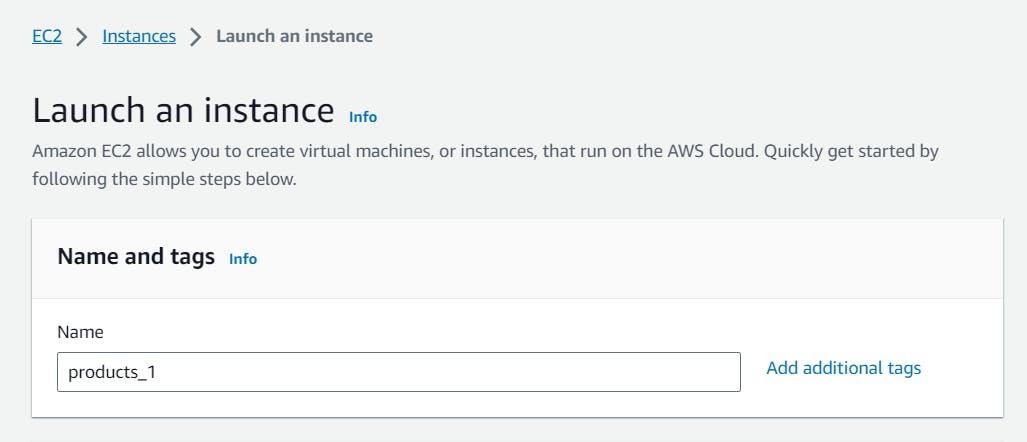
- Choose an Amazon Machine Image (AMI): Select an Amazon Linux AMI or your preferred Linux distribution.
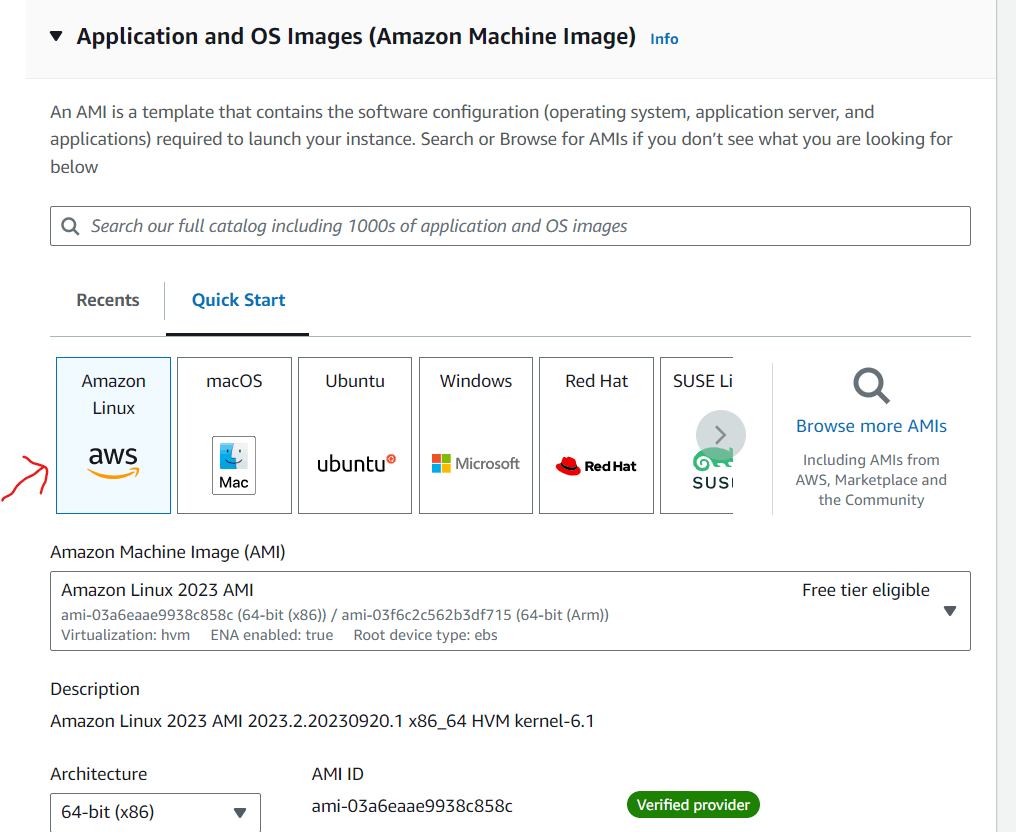
- Choose an instance type based on your requirements. I have selected for t2.micro
- Configure instance details (e.g., VPC, subnet, security group).

- Add User Data Script: In the "User data" field, enter the below script to updates the package repository, installs the Apache HTTP Server (httpd), starts the httpd service, configures it to start automatically on boot and create sample html file for the products_1 page
#!/bin/bash
yum update -y
yum install -y httpd
service httpd start
service httpd status
chkconfig httpd on
cd /var/www/html
mkdir products
cd /var/www/html/products
# Create an HTML file with a background color
cat <<EOF > index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Products_1 EC2 instance</title>
</head>
<body style="background-color: #F0E68C;"> <!-- Set the background color here -->
<h1>Products Page</h1>
<p>Welcome to Products_1 System in Target Group Products</p>
</body>
</html>
EOF
# Restart the Apache web server to apply changes
service httpd restart
- Launch the EC2 Instance: Review your instance settings and click "Launch."
Create products_2 EC2 instance:
- Give a name to the products_2 EC2 instance as products_2
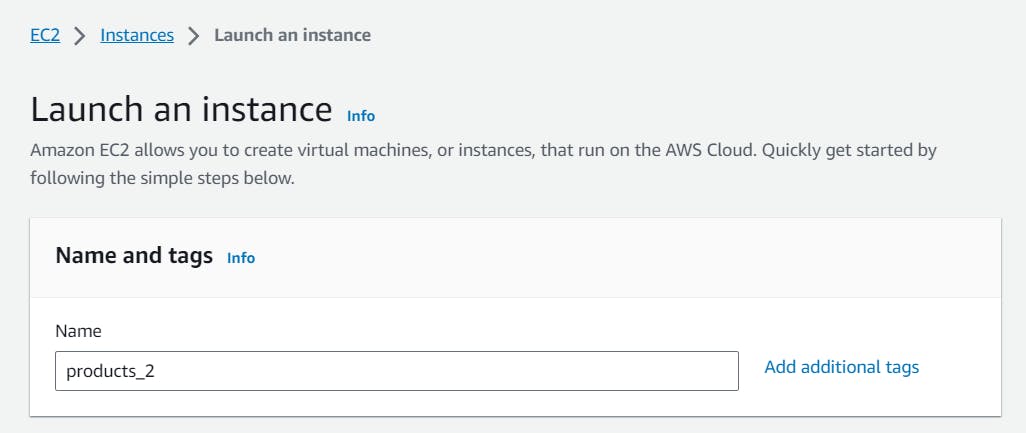
Follow the above steps to configure the further steps for creating the products_2 EC2 instance
Add User Data Script: In the "User data" field, enter the below script to updates the package repository, installs the Apache HTTP Server (httpd), starts the httpd service, configures it to start automatically on boot and create sample html file for the products_2 page
#!/bin/bash
yum update -y
yum install -y httpd
service httpd start
service httpd status
chkconfig httpd on
cd /var/www/html
mkdir products
cd /var/www/html/products
# Create an HTML file with a background color
cat <<EOF > index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Products_2 EC2 instance</title>
</head>
<body style="background-color: #F0E68C;"> <!-- Set the background color here -->
<h1>Products Page</h1>
<p>Welcome to Products_2 System in Target Group Products</p>
</body>
</html>
EOF
# Restart the Apache web server to apply changes
service httpd restart
Create orders_1 EC2 instance:
- Give a name to the orders_1 EC2 instance as orders_1
Follow the above steps to configure the further steps for creating the orders_1 EC2 instance
Add User Data Script: In the "User data" field, enter the below script to updates the package repository, installs the Apache HTTP Server (httpd), starts the httpd service, configures it to start automatically on boot and create sample html file for the orders_1 page
#!/bin/bash
yum update -y
yum install -y httpd
service httpd start
service httpd status
chkconfig httpd on
cd /var/www/html
mkdir orders
cd /var/www/html/orders
# Create an HTML file with a background color
cat <<EOF > index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Orders_1 EC2 instance</title>
</head>
<body style="background-color: #F0E68C;"> <!-- Set the background color here -->
<h1>Orders Page</h1>
<p>Welcome to Orders_1 System in Target Group Products</p>
</body>
</html>
EOF
# Restart the Apache web server to apply changes
service httpd restart
Create orders_2 EC2 instance:
Give a name to the orders_1 EC2 instance as orders_2
Follow the above steps to configure the further steps for creating the orders_2 EC2 instance
Add User Data Script: In the "User data" field, enter the below script to updates the package repository, installs the Apache HTTP Server (httpd), starts the httpd service, configure it to start automatically on boot and create sample html file for the orders_2 page
#!/bin/bash
yum update -y
yum install -y httpd
service httpd start
service httpd status
chkconfig httpd on
cd /var/www/html
mkdir orders
cd /var/www/html/orders
# Create an HTML file with a background color
cat <<EOF > index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Orders_2 EC2 instance</title>
</head>
<body style="background-color: #F0E68C;"> <!-- Set the background color here -->
<h1>Orders Page</h1>
<p>Welcome to Orders_2 System in Target Group Products</p>
</body>
</html>
EOF
# Restart the Apache web server to apply changes
service httpd restart
Step 2: Create Target Groups
Create a New Target Group for products-target-group:
Choose the "Target type", We can select Instances if we are routing traffic to the EC2 instances or we can select IP address if we need to choose a specific IP address or we can select Lambda Function or Application load balancer.
I am selecting Instances as I am routing my traffic to EC2 instances.
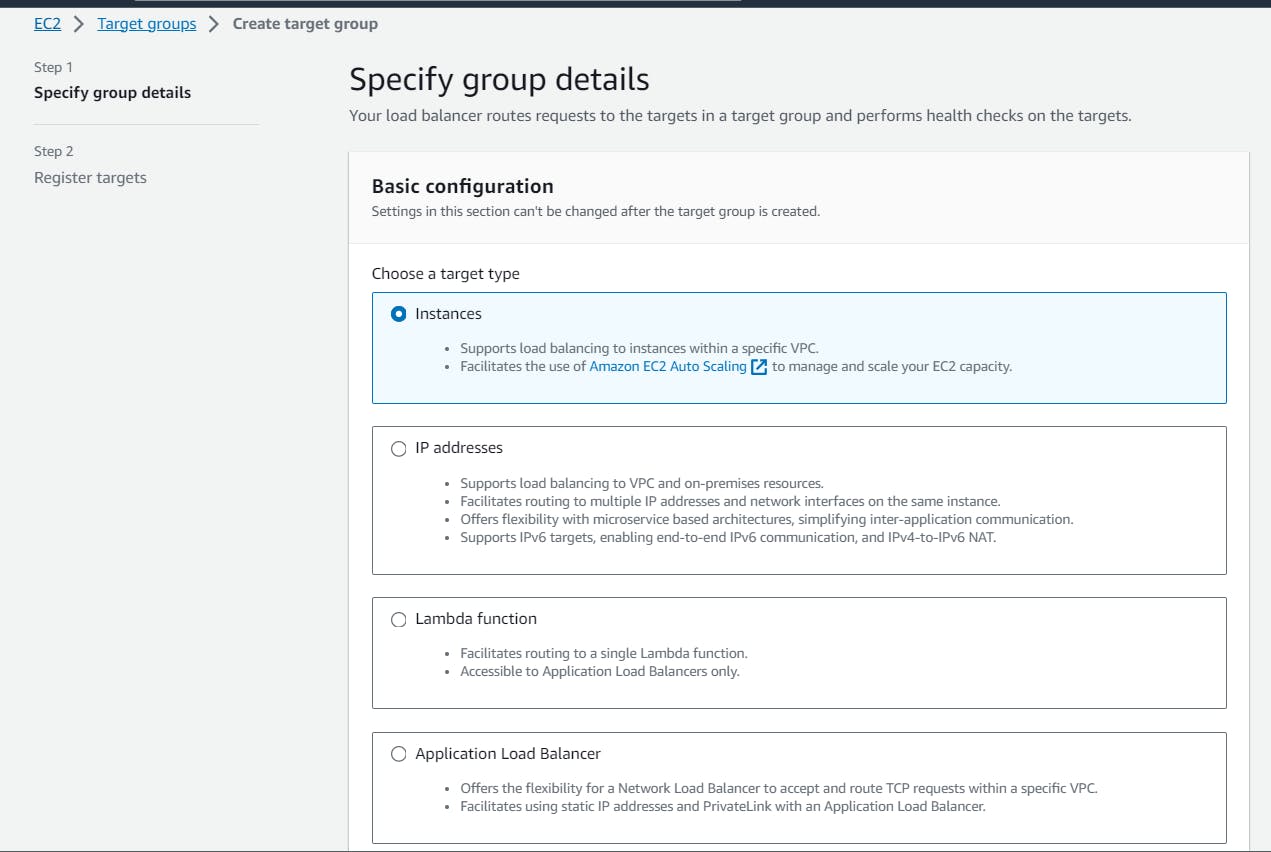
Click the "Create Target Group" button. Name it
products-target-groupand configure it like the below:- Specify the protocol and port (e.g., HTTP on port 80) as our application inside the EC2 instance running on port 80 with HTTP
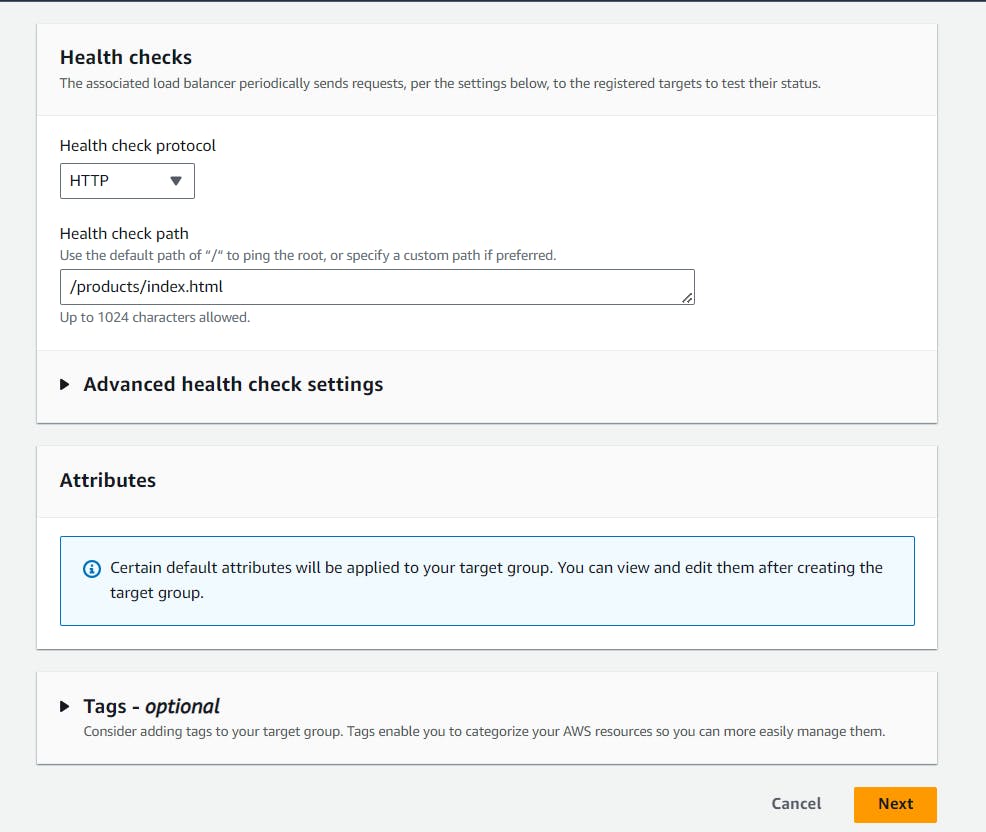
- Configure health checks: The associated load balancer periodically sends a request to the EC2 instance and checks the default path and registers the targets to test their status whether the EC2 instance is healthy or not
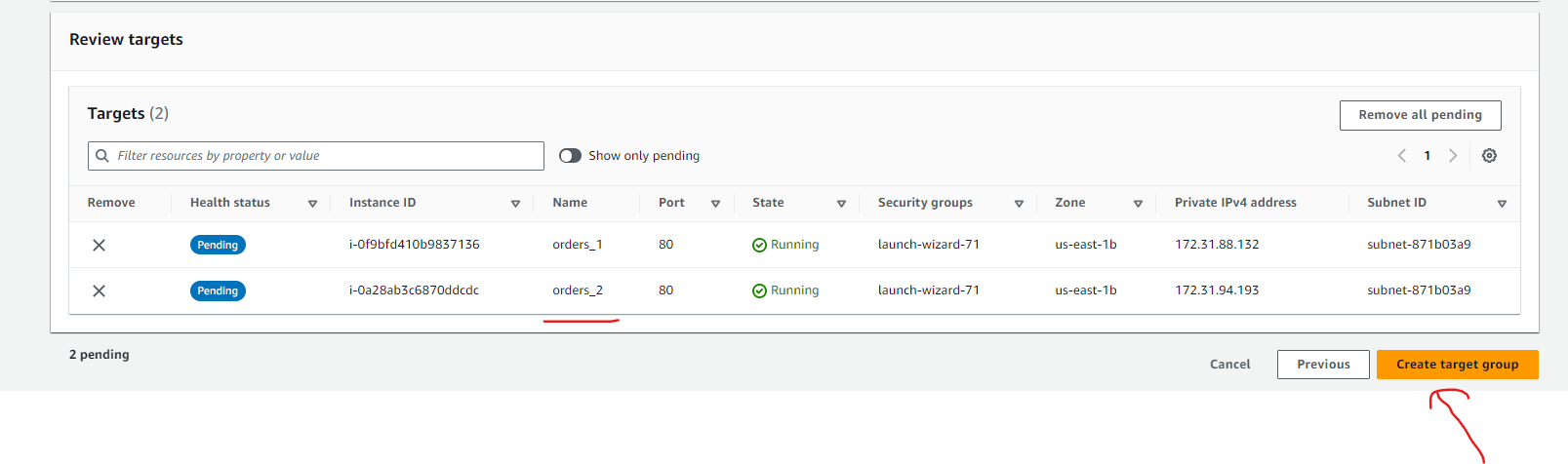
- Register Targets: Choose the EC2 instances which we want to associate with the products-target-group, and then the load balancer will send a request to the associated EC2 instances when a request comes to the /products URL and click on Include as pending below
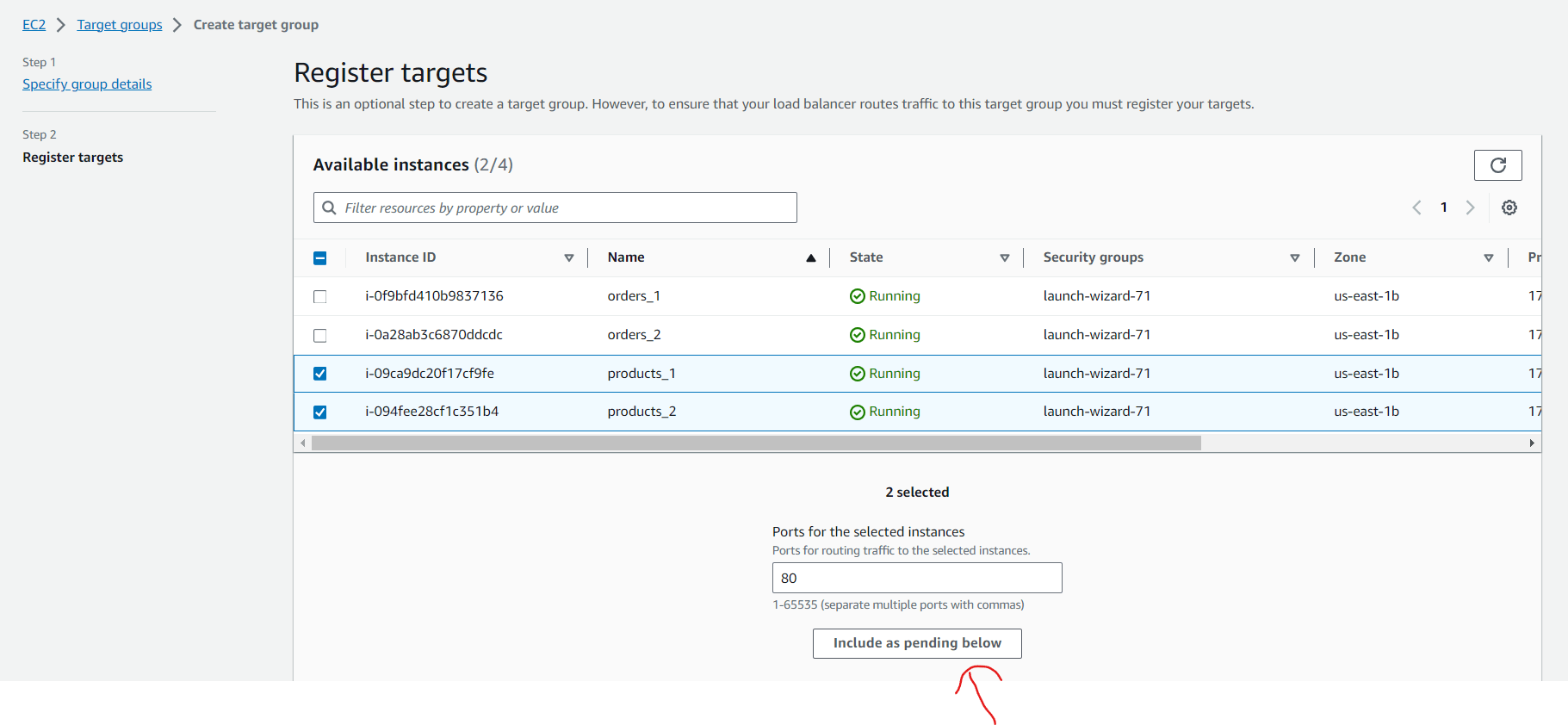
- Review Targets: Review the products EC2 instances targets and click on Create target group

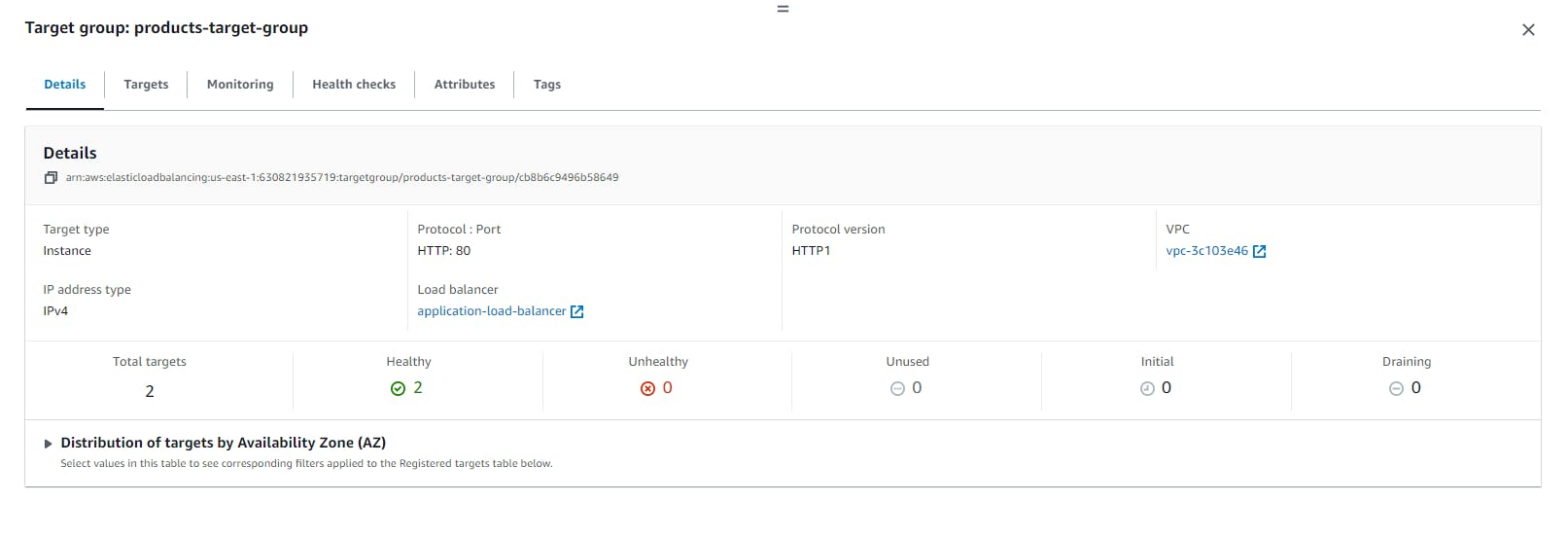
Create a New Target Group for orders-target-group:
Follow the above steps to configure the further steps for creating the orders-target-group
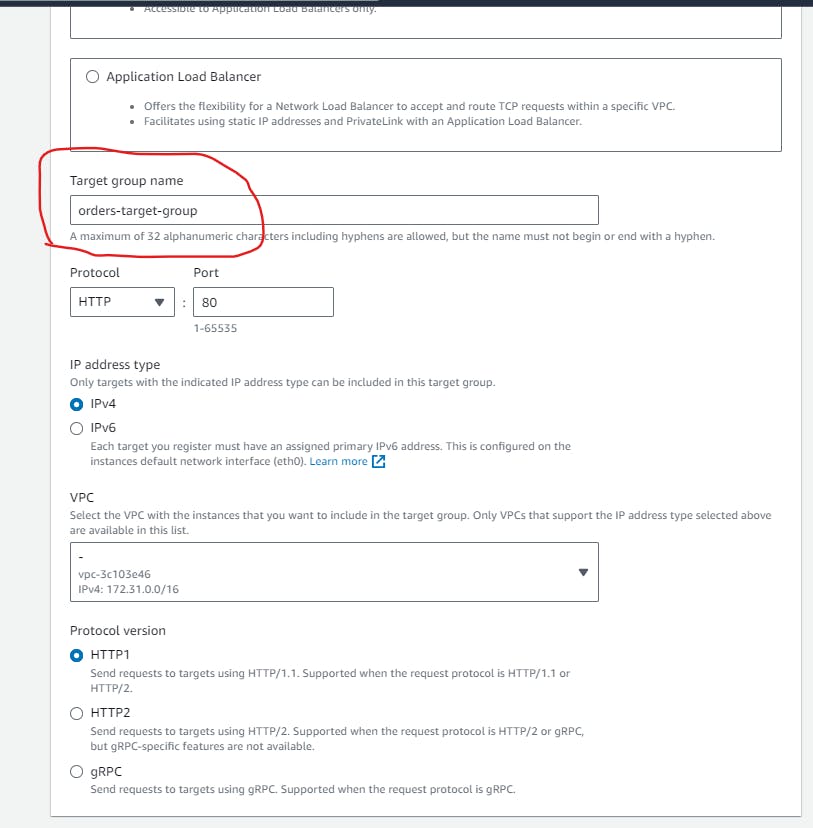
Click the "Create Target Group" button. Name it
orders-target-groupand configure it like the below:- Specify the protocol and port (e.g., HTTP on port 80) as our application inside the EC2 instance running on port 80 with HTTP
- Register Targets: Choose the EC2 instances which we want to associate with the orders-target-group, and then the load balancer will send a request to the associated EC2 instances when a request comes to the /orders URL and click on Include as pending below
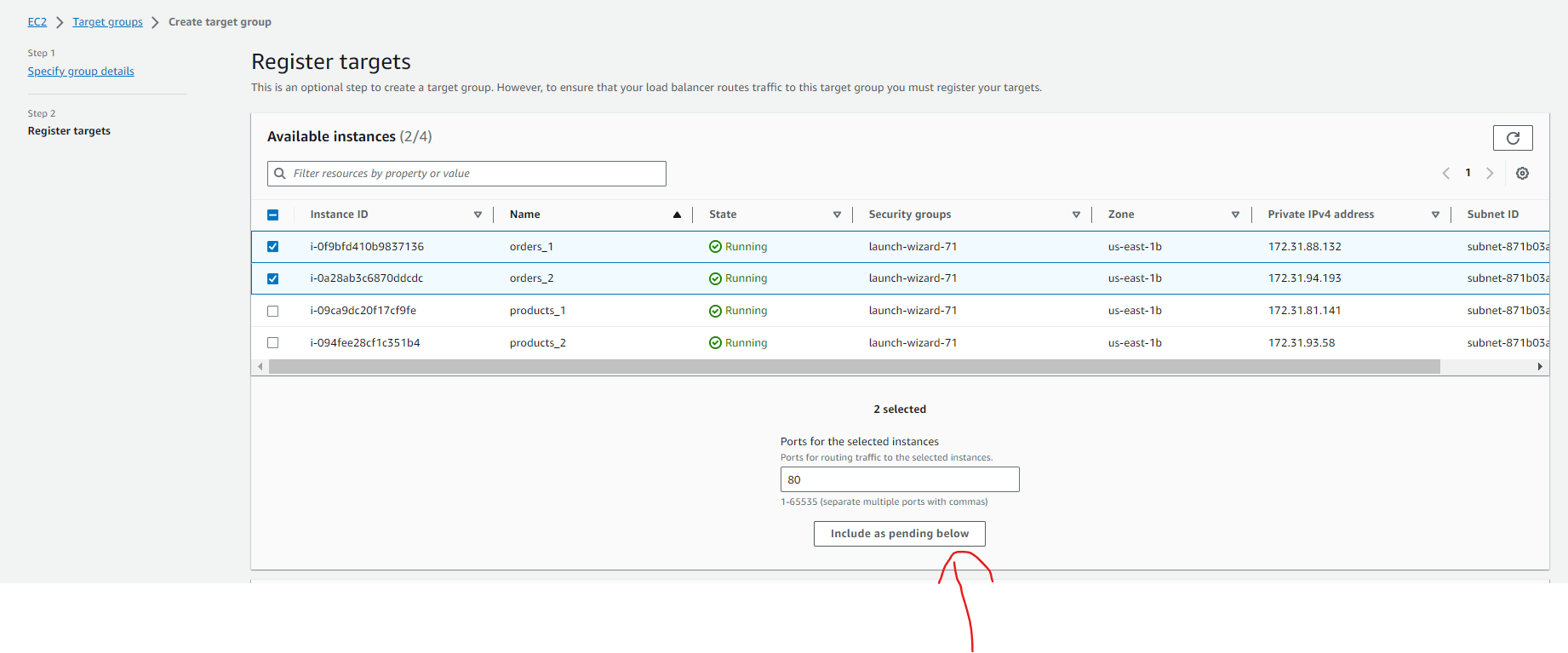
- Review Targets: Review the products EC2 instances targets and click on Create target group
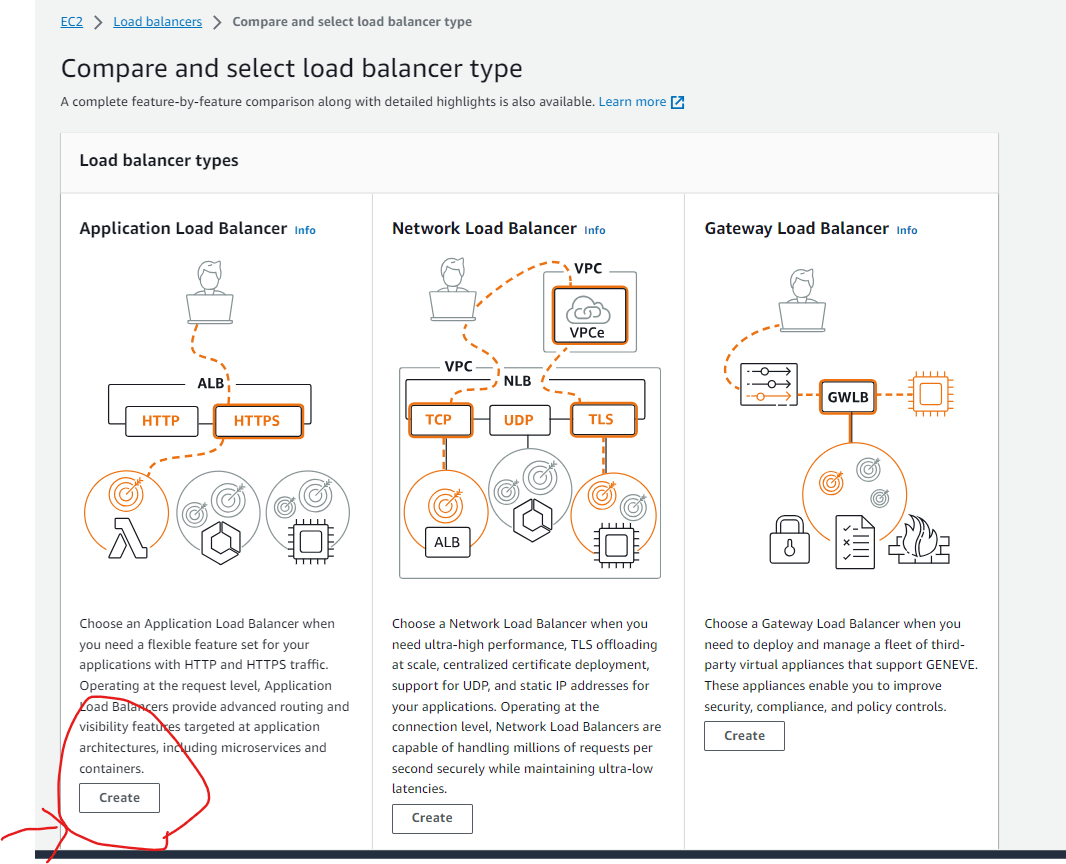
Step 3: Create an Application Load Balancer (ALB)
- Launch the Load Balancer Wizard:
- Click the "Create Load Balancer" button.
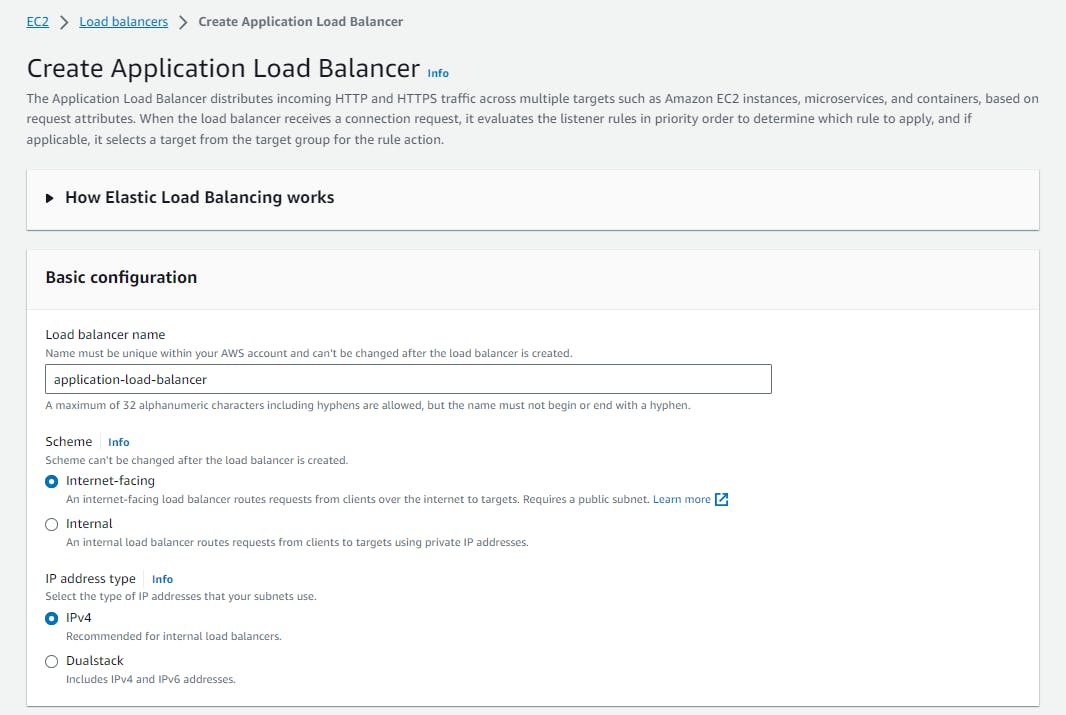
- Configure Basic Settings:
Fill out the following information:
Load Balancer Name: Give your ALB a descriptive name, e.g.,
application-load-balancer.Scheme: Choose "internet-facing" for public access.
IP Address Type: Select "ipv4" unless you have specific ipv6 requirements.
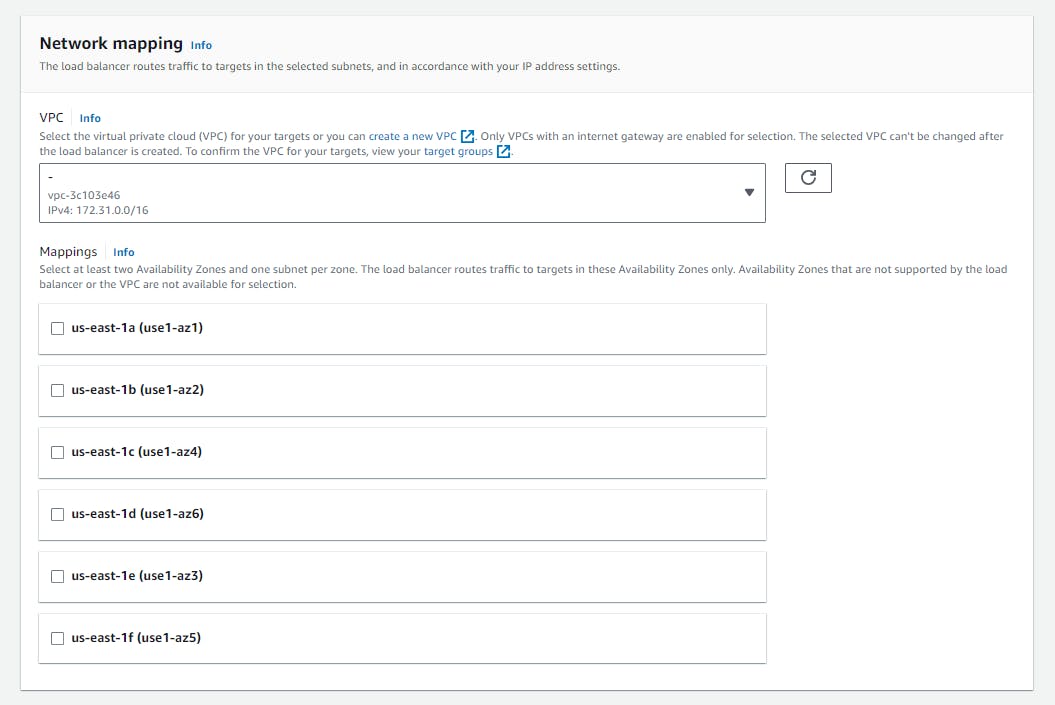
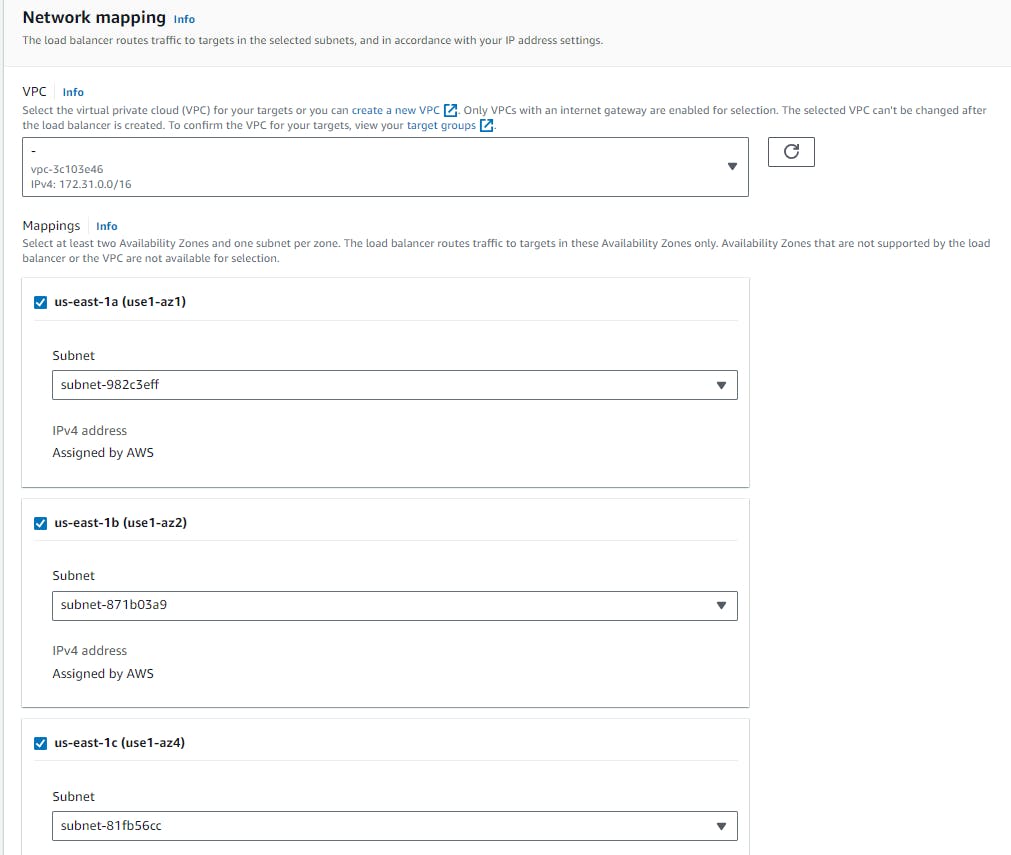
Network Mapping:
- Select at least 2 availability zones so that the load balancer will route the traffic to targets in those availability zones only
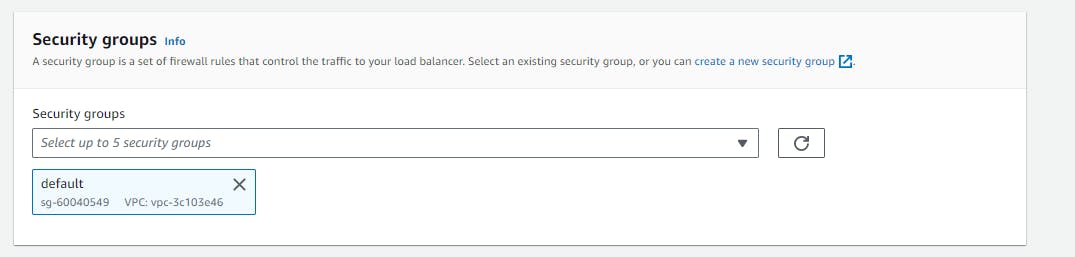
Configure Security Groups:
- Choose an existing security group or create a new one. This security group controls the inbound and outbound traffic for your ALB.


Configure Listeners:
Set up your listeners based on your application's requirements. For example:
Add a listener for HTTP (port 80) and HTTPS (port 443) if you're using SSL/TLS.
Add the target group name under the default action for forwarding the default requests to the specific target group

- Review Load Balancer: Review Configurations and Click on Create Load Balancer


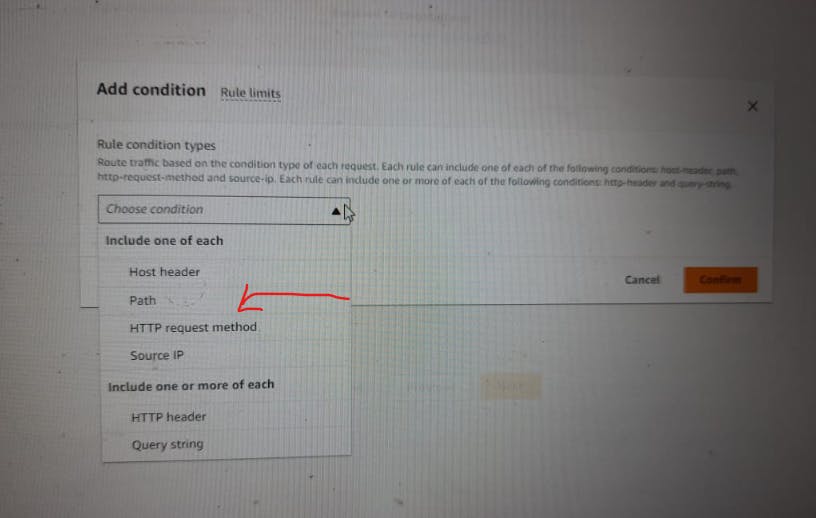
Step 4: Update Listener Rules
Configure Rules:
Go back to the "Listeners" tab of your ALB to configure rules
Configure rules to route traffic to the appropriate target group based on your application's needs.

For example, you can use path-based routing to route
/products/*to theproducts-target-groupand/orders/*to theorders-target-group.If we add rule /products/* and /orders/* if have any pages after that also it will work

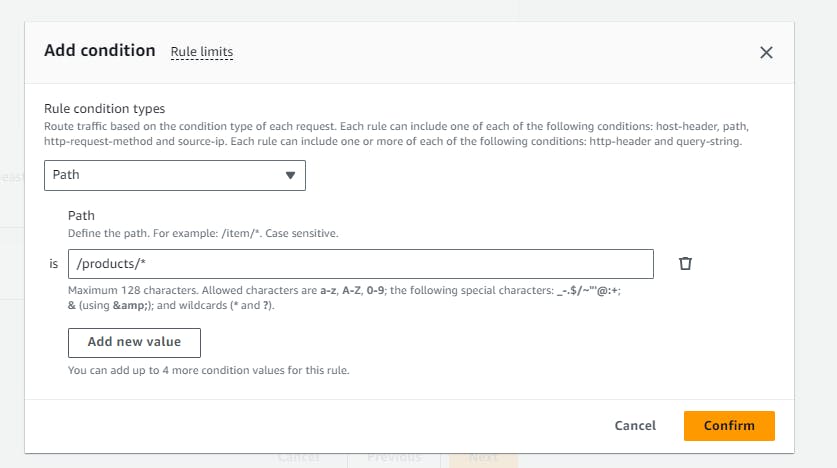





- Add the path-based routing to route to
/orders/*to theorders-target-groupsame as products-target-group. Follow the steps above for adding rule to the orders-rule




Save Changes:
- Save your listener configuration.

With these steps, successfully set up an Application Load Balancer on AWS, created two target groups, and registered EC2 instances in each target group. ALB is now ready to distribute traffic to the associated EC2 instances based on your defined rules.

Note: Load Balancers by default will follow the round-robin mechanism to distribute the traffic. In our example /products URL, we have defined 2 EC2 instances in the products-target-group so when we are accessing first time its giving Products_1 EC2 instance and after refresh its giving Products_2 EC2 instance.
Example 1 : loadbalancer-dns-name/products/


Example 2 : loadbalancer-dns-name/orders/
Same approach for /orders URL as well. we have defined 2 EC2 instances in the orders-target-group so when we are accessing first time its giving Orders_1 EC2 instance and after refresh its giving Orders_2 EC2 instance.


References:
- Checkout this blog to know more about User Data in the EC2 instance : https://sravya-yakkati.hashnode.dev/how-to-install-apache-http-server-httpd-on-amazon-ec2-with-user-data-script
